- By YIKONG
- 2025-05-09 14:16:55
- Industry Information
Industry News | Silicon-Based Employee Debut, AI Chip Competition, and Manufacturing Cost Reconstruction
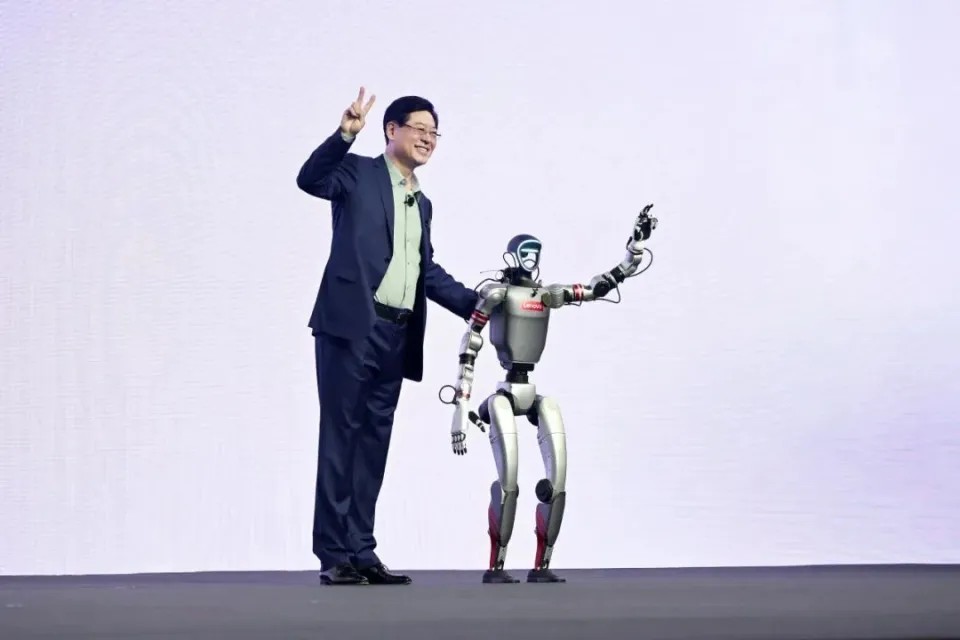
1.At the 2025 Lenovo Innovation Technology Conference, Lenovo Group officially launched its first “silicon-based employee” — the humanoid robot “Lenovo Lexiang No. 1,” marking a major breakthrough in mixed-mode artificial intelligence.
Equipped with the Lenovo Lexiang Super-Intelligent Agent, it features multimodal collaborative perception and interaction: it can complete multi-turn dialogue responses within 0.8 seconds, and fuses vision, speech and text-processing capabilities to query the enterprise knowledge base in real time for decision-making. In live demos, the robot not only performed Tai Chi smoothly but also demonstrated data-security safeguards—automatically avoiding privacy leaks when faced with sensitive information. Lenovo Chairman Yang Yuanqing emphasized that this achievement rests on a “device-edge-cloud-network” hybrid-computing infrastructure, which dynamically allocates compute resources to perform distributed inference, signaling that hybrid-AI technology has officially entered the industrial application stage. In addition, Lenovo unveiled a Super-Intelligent Agent Matrix covering individuals, enterprises and cities. Its “Tianxi” inference-acceleration engine uses high-performance parallel decoding and a heterogeneous computing architecture to dramatically boost on-device inference on AI PCs—able even to solve a gaokao math problem in 13 seconds, rivaling cloud-based large models.

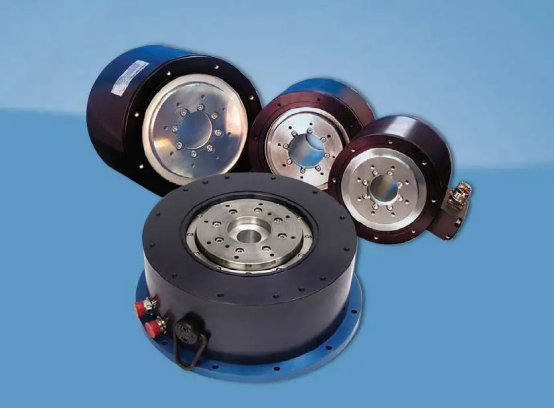
2.At the 2025 U.S. Robotics Summit, Kollmorgen Corporation launched the TBM2G series frameless servo motors designed specifically for collaborative robots, further solidifying its technical leadership in precision drives.
This series employs a high-torque-density design optimized for sub-48 V low-voltage scenarios, making it especially suitable for lightweight cobots. Its high-temperature capability is outstanding: even with a 155 °C winding temperature, it maintains full-power output, solving the heat-dissipation challenge under heavy loads. Moreover, the motors can be optionally equipped with integrated Hall sensors and, without increasing overall length, simplify installation—significantly enhancing system flexibility and reliability.

3.Mitsubishi Electric’s China-market brand “Lingling” introduced its first domestically designed LR1 series slim I/O modules, strengthening its footprint in industrial automation.
Developed by a China-based team, these modules emphasize a compact structure and high compatibility, easily adapting to various industrial control scenarios. This move reflects Mitsubishi Electric’s deepening localization strategy—responding to China’s import-substitution trend with tailored products. Analysts believe Lingling’s independent operation will help Mitsubishi Electric remain competitive in price-sensitive markets.

4.Collaborative-robot maker Yuejiang Technology has taken an equity stake in CAS Fifth Epoch, deepening the fusion of AI and robotics technologies.
CAS Fifth Epoch focuses on AI algorithms and intelligent robot R&D and has already completed tens of millions of yuan in seed and Series A financing. Yuejiang’s investment not only provides capital but is also expected to upgrade its cobots’ AI-driven autonomous-decision capabilities. Their joint efforts will likely target intelligent solutions for industrial inspection, logistics sorting and other scenarios—accelerating commercial deployment.
5.In 2024, NAURA Technology Group Co., Ltd. (North Microelectronic Huachuang) topped the A-share semiconductor industry with net profit of ¥5.621 billion, underscoring the domestic-substitution trend.
Its revenue rose 35% year-on-year to ¥29.838 billion, far outpacing competitors such as SMIC. Growth was driven by surging AI-chip demand and a consumer-electronics revival—particularly breakthroughs in etching and thin-film deposition equipment—which have secured critical roles in both logic and memory chip manufacturing. In Q1 2025, revenue grew a further 38%, highlighting the strong momentum of domestic semiconductor-equipment vendors in tech iteration and market penetration.

6.AMD is expected to lose $1.5 billion in 2025 due to U.S. export restrictions on chips to China, illustrating geopolitics’ impact on the tech industry.
Although its Q1 revenue rose 36% year-on-year to $7.44 billion—driven by strong data-center performance—the U.S. Commerce Department’s new rules require licenses for exporting advanced AI processors to China, directly affecting sales of the MI300 GPU series. AMD acknowledges that without licenses, some orders may shift to NVIDIA’s compliant products, further heightening market uncertainty.

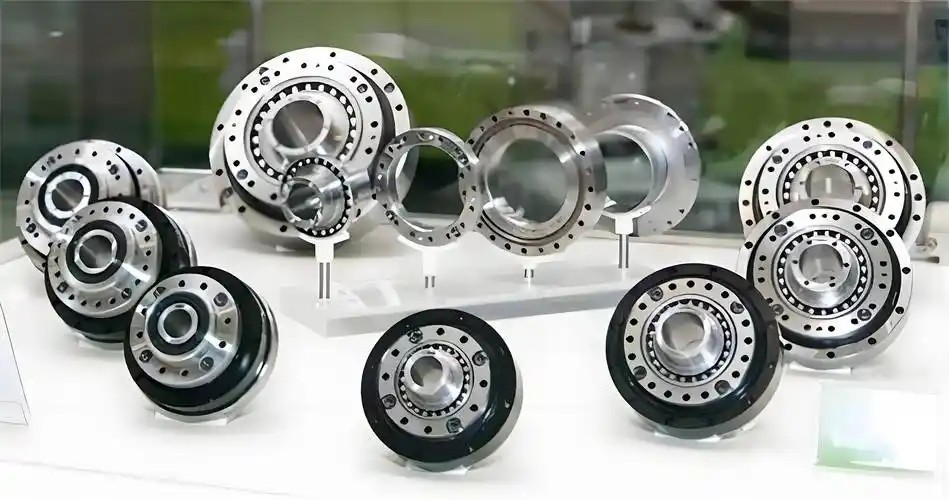
7.China’s demand for RV-type reducers for industrial robots is projected to reach 846,400 units by 2028, marking a critical phase for domestic replacement.
In 2024, consumption totaled 570,500 units (up 9.7% year-on-year). Domestic vendors such as Huandong Technology and Zhongda Lider are gradually overcoming technical bottlenecks. However, issues revealed in Huandong Technology’s IPO—such as supply-chain reliance on parent company Shuanghuan Transmission and related-party transaction premiums—have raised questions about the autonomy of domestic reducer technology. Despite the potential 8–12% cost savings from higher localization, Japanese maker Nabtesco still dominates 53% of the market. Analysts predict 2025 may become the turning point when domestically produced RV reducers enter foreign capital supply chains at scale—provided they can overcome stability and R&D challenges.