- By YIKONG
- 2025-03-10 14:32:09
- TECHNICAL
AGV on-site data analysis—steer wheel monitoring and maintenance
1. Debugging background and product information:
Debugging site: production line of a terminal-site automobile assembly workshop;
Testing machines: AGV vehicles No. 1, No. 2, No. 8;
Rudder motor parameters: 1000W of rated power of MRT20.0142, rated voltage of 48VDC, rated current of 26A, peak current of 70A, rated speed of 1700RPM, maximum working temperature of 110 degrees;
Driver parameters: maximum voltage 60VDC, rated current 60A; peak current 120A; maximum operating temperature 85 degrees;
The No. 1 AGV car traction motor was smoking.
Abstract of monitoring data of AGV vehicles in 2. No. 1, No. 2 and No. 8:
3. Preliminary analysis of normal operation monitoring data:
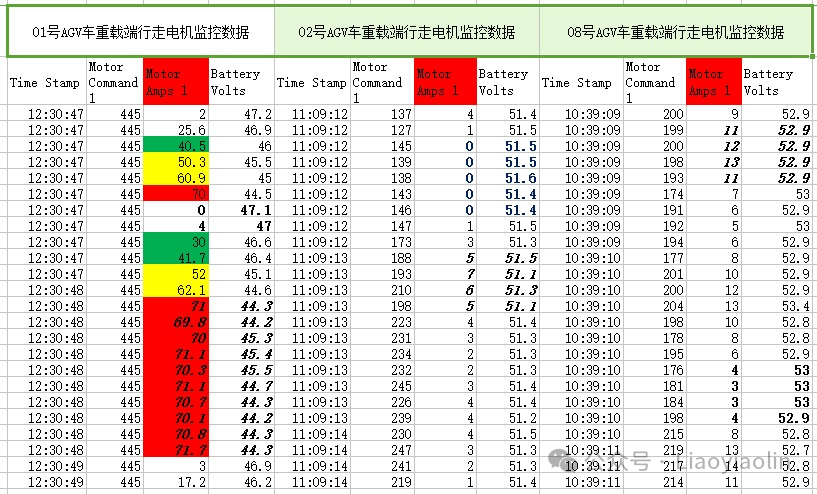
Through the summary of the monitoring data sheet, it was found that when walking in a normal straight line, the motor current fluctuated between a few amperes and a dozen amperes, which shows that the actual load rate of the motor is less than 50%, which shows that the motor and driver selection meet the linear operation requirements.
Through the summary of the monitoring data sheet, it is found that when the vehicle body moves horizontally, the maximum current peak can reach 70A (this parameter is set by the driver), and the normal duration is less than 2s. Explanation: The motor and driver selection meet the cross-transport operation requirements.
From the data summary table, it is not difficult to see that the influence of battery voltage on motor current during normal operation is crucial. When the battery voltage is lower than 48V, the motor drags the load to output a sufficiently large torque at the moment, causing the output current to increase sharply. Even under such low voltage harsh operating conditions, the motor overload is extremely small, which shows that the motor and driver are sufficient to cope with the maximum power output under transverse conditions.
Under the premise of monitoring the data of three motors that are operating normally, the motor will not overheat under normal circumstances. For this point, we can use a temperature infrared gun for inspection in future debugging and production processes. When the AGV car runs continuously for 20 minutes (about the motor thermal equilibrium time) or more, the maximum temperature data measured using the infrared gun, plus 5~10 degrees (about the heat transfer temperature difference between the motor wire and the case) is close to the actual temperature of the motor wire. This value is less than 110 degrees and can work stably for a long time. When the motor smoked twice, there was no abnormality in the subsequent test operation, which means that the motor performance is still reliable.
4. Trial analysis of one of the motors leaving the factory and overheating (smoking) during operation of No. 1 AGV vehicle:
The factory-abnormal motor cannot test the relevant data under the existing conditions, so it does not meet the prerequisites for analysis and judgment. It is skipped here; the overheated motor during operation is tried to analyze the following, and the possibilities are:
1. The motor is blocked, and the possible factors include incomplete release of the brake, which leads to overloading of the motor.
2. The speeds of the two motors are not synchronized, causing a "top bull" or "tug-of-war" trend, resulting in the motor being overloaded.
3. Ground obstacles cause the wheel to be stuck and the motor to be blocked. After an emergency shutdown for a period of time, the AGV vehicle will be removed by driving the AGV vehicle itself to eliminate the abnormal situation.
4. The operating trend of the two drive wheels is not on the same straight line, parallel line or concentric arc trajectory, resulting in the reduction of the combined force of the two motors and overload. The AGV is smoked after running more than 1 meter in a straight line, so this abnormal situation is also eliminated.
5. Insufficient battery output power, resulting in increased motor current, which in turn caused the motor to overheat. In subsequent tests, this phenomenon confirmed that the battery energy storage is seriously insufficient. In subsequent tests, it was also found that the No. 1 AGV car had insufficient energy storage.
6. The driver parameter settings are unreasonable or the fault causes the motor current to be uncontrolled, resulting in the motor current being too large and there is no timely protection. Note: This situation is more likely to occur when the driver is much larger than the motor.
7. The motor's own temperature protection function is missing or the function is not used.
8. Based on the above analysis, the confirmed cases of motor overload have been confirmed: the motor temperature protection function is not used; the driver's undervoltage and current limit protection function is not used; and the battery energy storage is seriously insufficient. It should be the main reason why the above three factors occur simultaneously and cause smoke from the No. 1 AGV car motor. Excluding any of the three factors will not cause the motor to be overloaded and smoke.
5. Handling measures or suggestions:

1. The driver undervoltage is set at 44~45V. When the battery energy storage is insufficient, the motor running speed is reduced and the output current is reduced (the protection mechanism is solidified by the driver and cannot be reset). That is to say, when the battery voltage is insufficient, the AGV car runs slowly until it stops running to protect the driver, motor, and battery pack.
Note: Before the motor smokes, some AGV cars do not have this protection function. It is recommended to make reasonable settings during subsequent debugging and running.
2. The driver current limit protection range is reasonably set. The current setting is peak current limiting 70A, and the current limit protection is 44A delayed 5000ms. When the output current exceeds 44A and lasts 5000ms, the driver will turn off the output until the running command is received again.
Note 1: Before the motor smokes, some AGV cars do not have this protection function! It is recommended to make reasonable settings during subsequent debugging and running.
Note 2: Parameters such as peak current, current limit protection and delay time can be adjusted and optimized in subsequent actual work.
3. The motor temperature protection function is not used. Before the motor smokes, the motor overheating signal is not used. It is recommended to use this function to effectively overheat protection for the motor.
4. The first point in the fourth point analysis cannot reproduce or restore the situation at that time. It is recommended to re-check and confirm to ensure that there is no poor contact or looseness after the machine vibrates; for the second point, it is also impossible to reproduce or restore the situation at that time. It is recommended to monitor the speed consistency of the two motors through the upper computer system, and intervene in a timely manner when the linear running speed difference is too large; for the driving wheel operation trajectory mentioned in point 4, the driving wheel operation trajectory or trend consistency problem should be optimized during subsequent debugging; for the fifth point, it is recommended to charge and replenish the power in time when the battery energy storage is reduced to ensure the normal and continuous operation of the AGV car.