- By YIKONG
- 2025-03-10 14:19:34
- TECHNICAL
Quickly understand the types and application scenarios of motors!
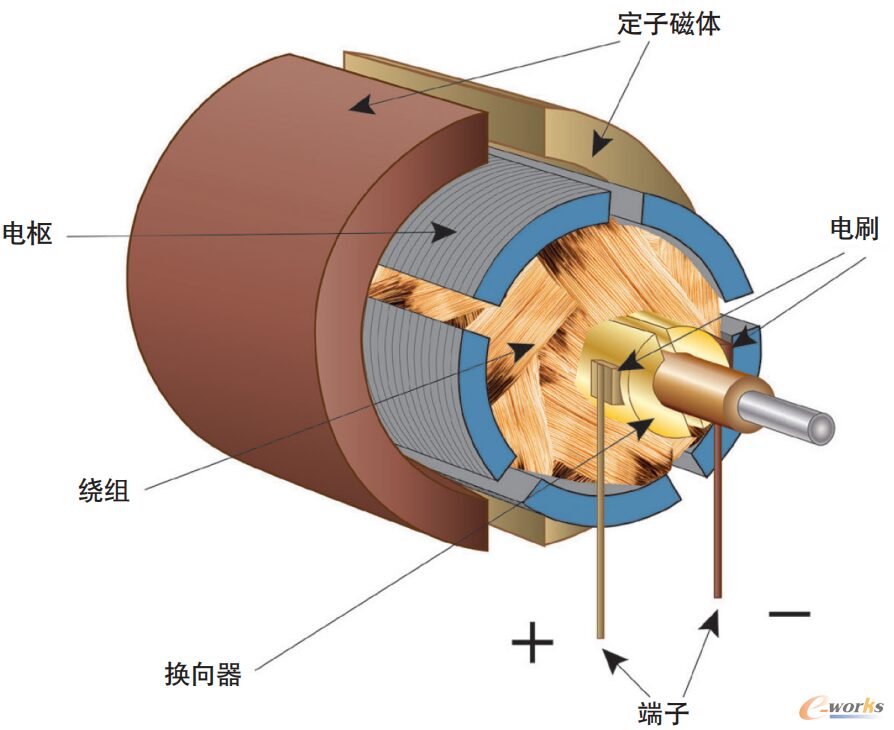
1. DC Motor
Features:
Simple structure and convenient control: the speed and torque can be controlled directly by adjusting the voltage or current.
Large starting torque: suitable for applications that require higher starting torque, such as electric vehicles, lifting equipment, etc.
High efficiency: It can still maintain high efficiency at low speeds.
High maintenance costs: The carbon brushes and commutators are prone to wear and need regular maintenance.
type:
Brushed DC motor (with carbon brush, frequent maintenance)
Brushless DC motor (no carbon brush, long life)
Application scenarios:
Electric vehicles, power tools, servo control systems, fans, robots, etc.
2. AC Motor
AC motors are a major category, including induction motors and synchronous motors.
Features:
Highly versatile: suitable for most industrial and civilian electric power drives.
Low maintenance cost: Compared with DC motors, there are no carbon brushes and commutators, and the maintenance is simple.
High efficiency and strong reliability: simple structure and low failure rate.
Classification:
Induction motor (asynchronous motor): Drives the rotor by electromagnetic induction, and the rotation speed is slightly lower than the synchronous speed.
Synchronous motor: The rotation speed is strictly proportional to the power supply frequency and operates at a constant speed.
Application scenarios:
Industrial equipment, household appliances, fans, water pumps, air conditioners, etc.

3. Induction Motor (Asynchronous Motor)
Features:
Simple and reliable: no carbon brush, commutator, less maintenance and long life.
Low starting torque: external starting method is required, such as capacitor start (single-phase) or inverter start (converter speed regulation).
Moderate efficiency: high efficiency during medium and high speed operation, but efficiency may decrease when load changes.
The speed is slightly lower than the synchronous speed: because the rotor needs a slip to induce the current.
Application scenarios:
Fans, water pumps, air conditioners, industrial equipment, conveyor belts, etc.
4. Synchronous Motor
Features:
Constant speed: The speed is strictly proportional to the power supply frequency, not affected by the load, and is suitable for precise control occasions.
High performance: High efficiency at full load, suitable for high power applications.
External excitation is required: Some synchronous motors require DC excitation (such as permanent magnet synchronous motors and synchronous generators).
Complex startup method: Inverters or additional startup devices are usually required.
Application scenarios:
Precision equipment, generators, large compressors, industrial automation, electric vehicles (permanent magnet synchronous motors), etc.

1. Universal Motor
Features:
AC or DC power supplies are available: Because the stator and rotor winding are connected in series, the current direction changes at the same time, it is suitable for AC/DC dual-purpose scenarios.
High speed, high power density: up to 10,000-30,000 RPM, suitable for high-speed applications.
Large starting torque: suitable for equipment that requires large starting torque.
Simple structure and low cost: but commutator and carbon brush are prone to wear, have a short life and high noise.
Application scenarios:
Vacuum cleaners, electric drills, hair dryers, mixers and other household appliances and power tools.
2. Permanent Magnet Motor (PM Motor)
Features:
No excitation winding, rotor with permanent magnets, improve efficiency and reduce energy loss.
High efficiency, high power density: especially suitable for new energy industries, such as electric vehicles, power tools, etc.
Small size and light weight: Reduces system complexity and is suitable for compact designs.
Low maintenance cost: no carbon brushes, long service life.
type:
Permanent magnet DC motor (PMDC): Similar to ordinary DC motors, the structure is simple.
Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM): efficient and precise control, widely used in new energy vehicles, wind power and other fields.
Brushless DC motor (BLDC): Commutated by electronics, no carbon brush, low noise and long life.
Application scenarios:
New energy vehicles (PMSM), home appliances (BLDC), wind power generation, model aircraft, electric bicycles, etc.

3. Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM)
Features:
The structure is extremely simple: no permanent magnet, no carbon brush, no commutator, and only the electromagnet is used to control the rotation.
Ultra-high reliability: suitable for harsh environments (such as high temperature and high humidity).
Wide speed ratio, emphasizes speed capability: suitable for variable speed drive applications.
High starting torque, low cost: but it is noisy and has obvious torque pulsation, requiring complex electronic control.
It is more efficient than induction motors, but the control system is complex and requires special control algorithms.
Application scenarios:
Electric vehicles, industrial transmission systems, washing machines, compressors, etc.

in conclusion:
If high-speed, large starting torque is required → single-phase series motor (such as power tools).
If you pursue high efficiency and long life → permanent magnet motors (such as electric vehicles, home appliances).
If high reliability is required and adapt to harsh environments, switch reluctance motors (such as industrial equipment, electric vehicles).